The Sun is the center of our solar system, and its importance cannot be overstated. It is responsible for the warmth and light that sustains life on Earth, and its magnetic field protects us from harmful cosmic radiation. In this article, we will explore the various aspects of the Sun, including its structure, composition, and atmosphere, as well as its impact on Earth and the future of sun exploration.
 |
| The Sun |
The Sun's Structure and Composition
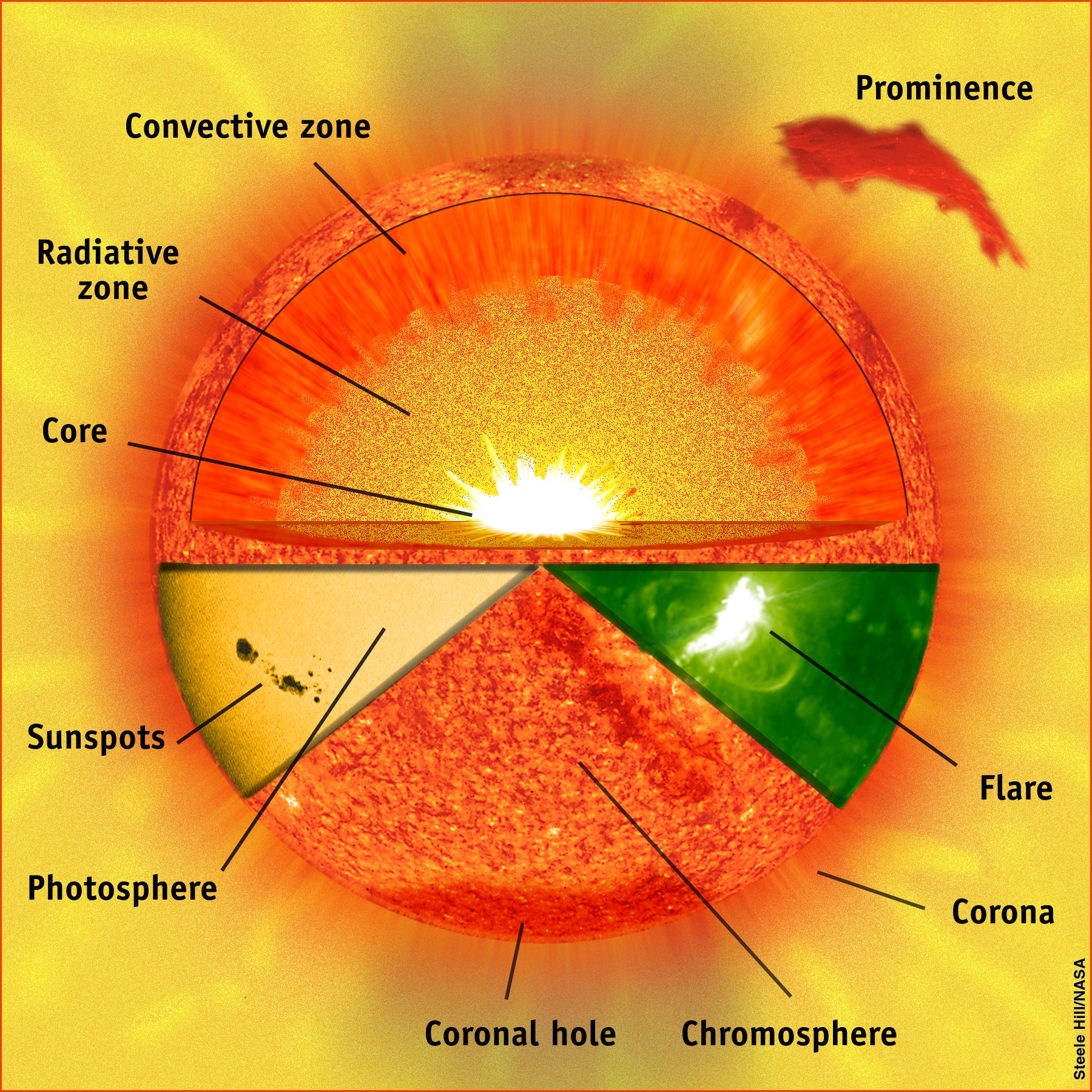
The Sun is a massive ball of gas, primarily made up of hydrogen and helium. It has a diameter of about 1.39 million kilometers and accounts for over 99% of the total mass of the solar system. The Sun's core, which makes up about 25% of its radius, is where nuclear fusion takes place. This process fuses hydrogen into helium, releasing energy in the form of light and heat.
Surrounding the core is the radiative zone, which accounts for about 45% of the Sun's radius. This zone is where the energy produced by nuclear fusion is transported outwards in the form of radiation. Beyond the radiative zone is the convective zone, which makes up about 30% of the Sun's radius. In this zone, hot plasma rises, and cooler plasma sinks, creating a pattern of convection that transports energy to the Sun's surface.
The Sun's atmosphere is divided into three main layers: the photosphere, the chromosphere, and the corona. The photosphere is the visible surface of the Sun and has a temperature of about 5,500°C. It is in this layer that sunspots, cooler areas on the surface of the Sun, are visible. The chromosphere, which is above the photosphere, is a layer of gas that has a reddish glow. The corona, which extends millions of kilometers into space, is the outermost layer of the Sun's atmosphere and is visible during a solar eclipse.
 |
| The Sun's Structure and Composition |
The Sun's Atmosphere
The Sun's atmosphere is a complex and dynamic system that is responsible for a range of phenomena, including solar wind, sunspots, solar flares, and coronal mass ejections. The solar wind is a stream of charged particles that flows outward from the Sun and affects the entire solar system. It is produced by the Sun's atmosphere and its magnetic field.
Sunspots are cooler areas on the surface of the Sun that appear darker than the surrounding areas. They are caused by the Sun's magnetic field and are often associated with solar flares and coronal mass ejections. Solar flares are intense bursts of radiation that occur near sunspots and can cause disruptions to radio communications and other technologies on Earth. Coronal mass ejections are huge bubbles of gas and magnetic field that are ejected from the Sun's corona and can also cause disruptions to Earth's technology.
 |
| The Sun's Atmosphere |
The Sun's Impact on Earth
The Sun's radiation and solar wind have a significant impact on Earth's atmosphere and climate. The Earth's magnetic field, which is shaped by the Sun's magnetic field, protects us from most of the harmful effects of the Sun's radiation. However, during times of increased solar activity, such as during a solar flare or coronal mass ejection, the Earth's magnetic field can be overwhelmed, leading to disruptions in radio communications and other technologies.
Space weather, which is caused by the Sun's activity, can also have a significant impact on our technology and infrastructure. For example, in 1859, a massive solar storm known as the Carrington Event caused widespread disruption to telegraph systems around the world. If a similar event were to occur today, it could potentially cause much greater damage to our technology-dependent society.
The Sun also has a direct impact on Earth's climate. Solar activity, such as sunspots, has been shown to have a small but measurable effect on global temperatures. However, the effect is small compared to the impact of human activities such as burning fossil fuels, which release greenhouse gases into the atmosphere.
 |
| The Sun's Impact on Earth |
The Future of Sun Exploration
Despite being our closest star, there is still much we do not know about the Sun. Scientists continue to study the Sun in order to better understand its behavior and its impact on our solar system. In recent years, there have been several notable missions to study the Sun up close.
In 2018, NASA launched the Parker Solar Probe, which will fly closer to the Sun than any previous spacecraft. The mission aims to study the Sun's magnetic field and the processes that heat the corona. Another notable mission is the Solar Orbiter, a joint mission between NASA and the European Space Agency (ESA) that launched in 2020. The Solar Orbiter will study the Sun's polar regions and provide new insights into the Sun's magnetic field.
In addition to these missions, there are several proposed missions that aim to study the Sun in even greater detail. These missions include the SunRISE mission, which would use a constellation of six small satellites to study the Sun's magnetic field, and the Solar-C mission, a joint mission between NASA and JAXA, which aims to study the Sun's corona in unprecedented detail.
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/1d/10/1d10ad86-c334-457a-abae-b1a5bb02aa85/solar_orbiter_and_parker_solar_probe_web.jpg) |
| The Future of Sun Exploration |
Conclusion
The Sun is a fascinating and vital part of our solar system. Its structure, composition, and behavior continue to captivate scientists and inspire space exploration. As we continue to study the Sun and its impact on Earth, we gain new insights into our place in the universe and the forces that shape our world.
For space enthusiasts and those who are interested in astronomy, the Sun is a fascinating subject to explore. It's also a great starting point for those who are new to astronomy and want to learn more about our solar system.
If you're interested in observing the Sun, it's important to take proper precautions. Looking directly at the Sun can cause permanent eye damage, so it's important to use proper solar viewing equipment. Specialized solar filters for telescopes, binoculars, and cameras are readily available for safe solar viewing.
In addition to observing the Sun, there are many ways to learn more about this fascinating star. Books, documentaries, and online resources can provide a wealth of information about the Sun's structure, behavior, and impact on our planet.
In conclusion, the Sun is a crucial component of our solar system and a fascinating subject of study. It provides light and heat to sustain life on Earth, but also has the potential to cause major disruptions to our technology and infrastructure. Continued research and exploration of the Sun will help us better understand its impact on our planet and inform our efforts to mitigate the risks of space weather.


0 Comments