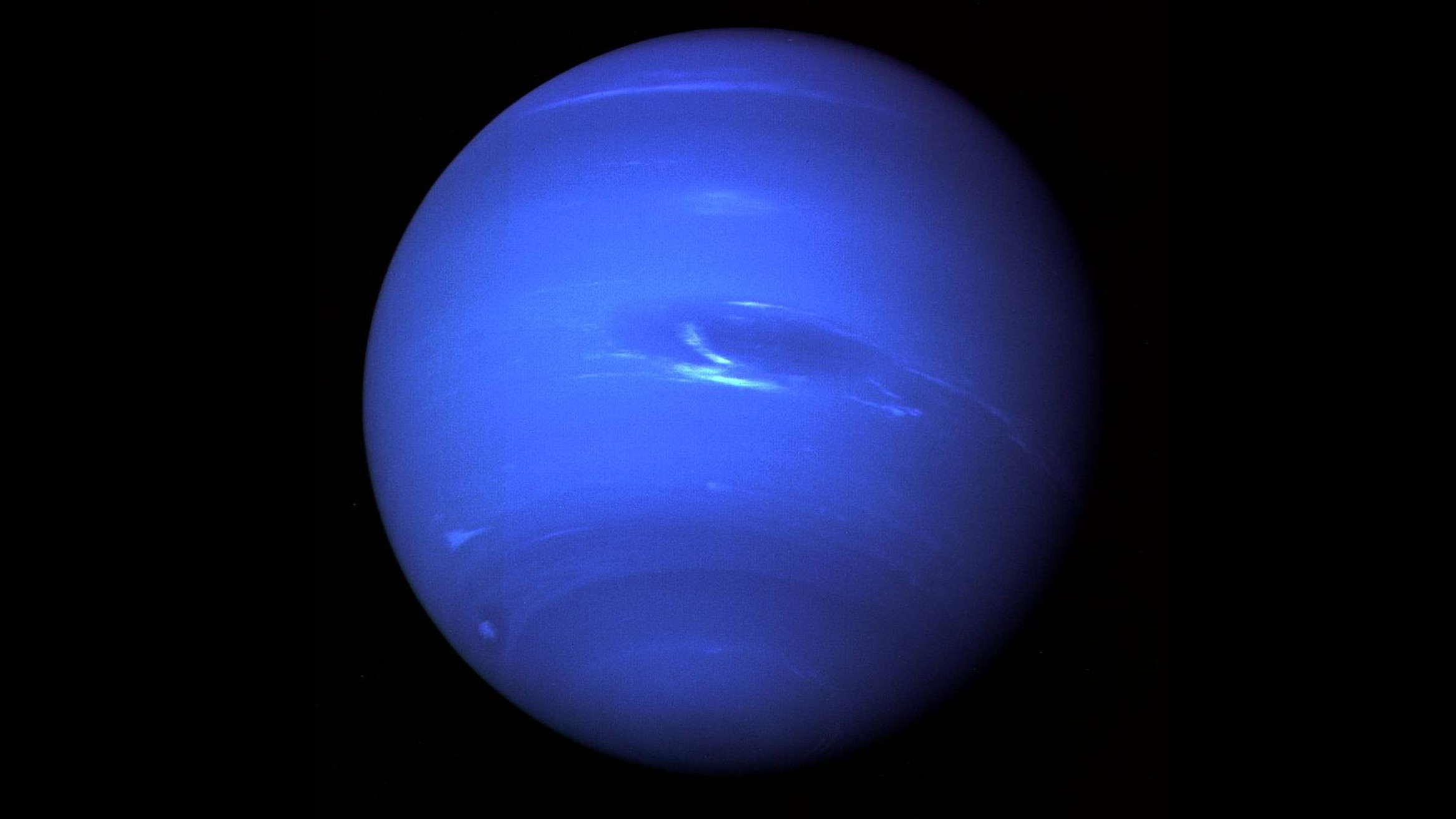
Neptune is the eighth planet from the sun and the farthest planet from Earth in our solar system. Named after the Roman god of the sea, Neptune is a gas giant that is almost four times the size of Earth and is known for its beautiful blue hue. In this article, we will dive into everything you need to know about Neptune, from its discovery to its composition, and its unique features.
 |
| Everything You Need to Know About Neptune |
Discovery and Naming of Neptune
Neptune was discovered in 1846 by French mathematician Urbain Le Verrier, who had predicted its existence based on observations of the orbit of Uranus. Le Verrier's calculations showed that the gravitational influence of an unknown planet was causing Uranus' orbit to deviate from its predicted path. Using this information, German astronomer Johann Galle was able to locate Neptune in the night sky just days after Le Verrier's prediction.
The planet was named Neptune after the Roman god of the sea, due to its deep blue color. In Roman mythology, Neptune was the brother of Jupiter and Pluto and was responsible for earthquakes and tides.
Physical Characteristics of Neptune
Neptune is the fourth-largest planet in our solar system, behind Jupiter, Saturn, and Uranus. It has a diameter of 49,244 km, making it almost four times larger than Earth. The planet's mass is 17 times that of Earth, and it is 30 times farther away from the sun than our planet.
Neptune is classified as a gas giant, along with Jupiter, Saturn, and Uranus. The planet is composed mainly of hydrogen, helium, and methane, and has a thick atmosphere that is believed to extend for thousands of kilometers. The planet's atmosphere is also known for its high-speed winds, which can reach speeds of up to 2,100 km/h.
Neptune's Magnetic Field
One of the most unique features of Neptune is its magnetic field. Unlike Earth's magnetic field, which is generated by the planet's molten core, Neptune's magnetic field is believed to be generated by a layer of electrically conducting fluid beneath its atmosphere.
The planet's magnetic field is also tilted at an angle of 47 degrees from its rotational axis, which is much greater than the 11-degree tilt of Earth's magnetic field. This results in a unique magnetic field that is offset from the planet's center and causes it to interact with the solar wind in a unique way.
Moons of Neptune
Neptune has 14 known moons, the largest of which is Triton. Triton is an icy moon that is believed to have been captured by Neptune's gravity. It has a diameter of 2,700 km and is one of the coldest objects in our solar system, with a surface temperature of -235°C.
 |
| Moons of Neptune |
Another interesting moon of Neptune is Nereid, which has an irregular shape and is believed to have been formed from debris left over from the formation of the solar system. Other moons of Neptune include Proteus, Larissa, and Despina.
Neptune's Rings
Neptune also has a system of rings, although they are much fainter than the rings of Saturn. The rings are composed mainly of dust and small rocks and are believed to have been formed from debris left over from the formation of Neptune's moons.
The rings of Neptune were first discovered in 1984 by the Voyager 2 spacecraft, which also provided the first close-up images of the planet and its moons. The rings are divided into five distinct bands, each of which is named after one of the moons of Neptune.
Exploration of Neptune
Neptune has only been visited by one spacecraft, the Voyager 2 probe, which flew by the planet in 1989. During its flyby, the spacecraft provided the first close-up images of the planet, its moons, and its rings.
Since then, there have been no other missions to Neptune, but there have been proposals for future missions, including a potential flagship mission that would involve sending a spacecraft to orbit Neptune and study its atmosphere, magnetic field, and moons in detail.
Conclusion
Neptune is a fascinating planet that is unique in many ways. From its discovery by Urbain Le Verrier to its beautiful blue hue and its unique magnetic field, Neptune is a planet that continues to capture the imagination of scientists and space enthusiasts alike.
While we have learned a great deal about Neptune from the Voyager 2 mission, there is still much to learn about this distant gas giant. With future missions, we may be able to unlock more of the secrets of this fascinating planet and gain a better understanding of how it fits into the complex system of our solar system.


0 Comments